BigInteger & BigDecimal 사용법 및 정리
BigInteger 자료형
BigInteger 사용되는 경우
| Type | 범위 |
| int | -2,147,483,648 ~ 2,147,483,647 |
| long | -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 ~ 9,223,372,036,854,775,807 |
- 자바의
int 메모리 크기는 4byte로 표현할 수 있는 범위는 -2,147,483,648 ~ 2,147,483,647이고
long 메모리 크기는 8byte로 표현할 수 있는 범위는 -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 ~ 9,223,372,036,854,775,807 입니다. - 이 타입의 범위를 넘어서게 된다면 에러가 발생하게 됩니다.
- 따라서 정수형 데이터의 타입을 사용할 때에는 반드시 자신이 사용하고자 하는 데이터의 최소 / 최대 크기를 교려해야 합니다.
- 만약 해당 타입이 표현할 수 있는 범위를 벗어난 데이터를 저장하게 된다면, 오버플로우(overflow)가 발생해 전혀 다른 값이 저장될 수 있기 때문입니다.
- 오버플로우 : 해당 타입이 표현할 수 있는 최대 표현 범위보다 큰 수를 저장할 때 발생하는 현상입니다.
- 언더플로우 : 해당 타입이 표현할 수 있는 최소 표현 범위보다 작은 수를 저장할 때 발생하는 현상입니다.
-
byte max = 128; byte min = -129; // 에러 발생 - 자바에서 byte 타입이 표현할 수 있는 정수 크기 범위는 -128 ~ 127까지입니다.
- 위 코드처럼 바이트 타입 변수의 크기보다 큰 범위를 저장하게 된다면 오버플로우, 언더플로우가 발생합니다.
- 그래서 프로그램 개발할 때 아주 큰 정수를 다룰 경우가 있을 때, 고정된 타입보다는 자바에서 제공하는 BigInteger라는 클래스를 활용하는 것이 좋습니다.
- BigInteger 자료형은 거의 무한한 크기의 정수형 숫자를 다룰 수 있는 타입입니다.
- 보안 및 암호화 응용 프로그램에서 널리 사용됩니다.
BigInteger 사용법
1. BigInteger 선언
- long타입이 수용할 수 있는 범위보다 더 큰 숫자가 필요하다면 BigInteger 클래스 타입을 사용하면 됩니다.
- 먼저 BigInteger를 사용하기 위해서 가장 먼저 java.math 패키지에서 클래스를 import 해야합니다.
- 기본적으로 BigInteger를 초기화 하기 위해서 문자열을 인자 값으로 넘겨주어야 합니다.
- 만일 숫자로 초기화 하려면 valueOf static 메서드를 이용하면 됩니다.
- 숫자로 선언하는 경우에도 int와 long의 범위를 벗어나면 안되기 때문에 큰 수를 저장하기 위해서는 문자열로 선언해야 합니다.
- 사용 예시
더보기
import java.math.BigInteger; public class BigIntegerBigDecimal { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("\n-----------------BigInteger 선언-----------------"); BigIntegerClass bigIntegerClass = new BigIntegerClass(); bigIntegerClass.bigInteger(); } } class BigIntegerClass { public void bigInteger() { // 문자열로 생성 BigInteger strBigInteger = new BigInteger("111111111111111111111"); System.out.println("문열로 선언 : " + strBigInteger); // 숫자로 생성 BigInteger numBigInteger = BigInteger.valueOf(222222222); System.out.println("숫자로 선언 : " + numBigInteger); // n진수로 생성 BigInteger nBigInteger1 = new BigInteger("FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF", 16); // 16진수 System.out.println("16진수로 선언 : " + nBigInteger1); BigInteger nBigInteger2 = new BigInteger("00010010010010001111", 2); System.out.println("2진수로 선언 : " + nBigInteger2); } } /* 출력 -----------------BigInteger 선언----------------- 문열로 선언 : 111111111111111111111 숫자로 선언 : 222222222 16진수로 선언 : 79228162514264337593543950335 2진수로 선언 : 74895 */
2. BigInteger 형 변환
- 문자열 리터럴 값으로 초기화할 수도 있지만, 이미 있는 숫자값들을 가져와 BigInteger 타입으로 형 변환도 가능합니다.
- 사용 예시
더보기
import java.math.BigInteger; public class BigIntegerBigDecimal { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("\n-----------------BigInteger 형 변환-----------------"); BigIntegerTypeConversion bigIntegerTypeConversion = new BigIntegerTypeConversion(); bigIntegerTypeConversion.bigInteger(); } } class BigIntegerTypeConversion { public void bigInteger() { // int / long -> BigInteger int num = 1000000000; BigInteger bigInteger = BigInteger.valueOf(num); System.out.println("int -> BigInteger : " + bigInteger); // BigInteger -> int int int_BigInt = bigInteger.intValue(); System.out.println("BigInteger -> int : " + int_BigInt); // BigInteger -> long long long_BigLog = bigInteger.longValue(); System.out.println("BigInteger -> long : " + long_BigLog); // BigInteger -> float float float_BigFloat = bigInteger.floatValue(); System.out.println("BigInteger -> float : " + float_BigFloat); // BigInteger -> double double double_BigDouble = bigInteger.doubleValue(); System.out.println("BigInteger -> double : " + double_BigDouble); // BigInteger -> String String string_BigString = bigInteger.toString(); System.out.println("BigInteger -> String : " + string_BigString); } } /* 출력 -----------------BigInteger 형 변환----------------- int -> BigInteger : 1000000000 BigInteger -> int : 1000000000 BigInteger -> long : 1000000000 BigInteger -> float : 1.0E9 BigInteger -> double : 1.0E9 BigInteger -> String : 1000000000 */
3. BigInteger 연산
- BigInteger 자료형은 클래스 구조이며 문자열이기 때문에 일반적인 +, -, * 기호를 이용한 사칙연산을 직접적으로 할 수 없습니다.
- 그래서 BigInteger 타입의 숫자 연산을 위해서 내장 메서드를 활용해야 합니다.
- 내장 메서드에는 대표적으로 add, substract, multiply, divide, remainder 등이 있습니다.
-
메서드 설명 BigInteger add(BigInteger val) 덧셈 (this + val) BigInteger subtract(BigInteger val) 뺄셈 (this - val) BigInteger multiply(BigInteger val) 곱셈 (this * val) BigInteger divide(BigInteger val) 나눗셈 (this / val) BigInteger remainder(BigInteger val) 나머지 (this % val) - 사용 예시
더보기
import java.math.BigInteger; public class BigIntegerBigDecimal { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("\n-----------------BigInteger 선언-----------------"); BigIntegerDeclaration bigIntegerDeclaration = new BigIntegerDeclaration(); bigIntegerDeclaration.bigInteger(); System.out.println("\n-----------------BigInteger 형 변환-----------------"); BigIntegerTypeConversion bigIntegerTypeConversion = new BigIntegerTypeConversion(); bigIntegerTypeConversion.bigInteger(); System.out.println("\n-----------------BigInteger 연산-----------------"); BigIntegerCalculation bigIntegerCalculation = new BigIntegerCalculation(); bigIntegerCalculation.binInteger(); } } class BigIntegerBitCalculation { public void bigInteger } class BigIntegerCalculation { public void binInteger() { BigInteger bigInteger = new BigInteger("111111111111"); BigInteger bigInteger1 = new BigInteger("111111111111"); System.out.println("덧셈 BigInteger.add : " + bigInteger.add(bigInteger1)); System.out.println("뺄셈 BigInteger.subtract : " + bigInteger.subtract(bigInteger1)); System.out.println("곱셈 BigInteger.multiply : " + bigInteger.multiply(bigInteger1)); System.out.println("나눗셈 BigInteger.divide : " + bigInteger.divide(bigInteger1)); System.out.println("나머지 BigInteger.remainder : " + bigInteger.remainder(bigInteger1)); } } class BigIntegerTypeConversion { public void bigInteger() { // int / long -> BigInteger int num = 1000000000; BigInteger bigInteger = BigInteger.valueOf(num); System.out.println("int -> BigInteger : " + bigInteger); // BigInteger -> int int int_BigInt = bigInteger.intValue(); System.out.println("BigInteger -> int : " + int_BigInt); // BigInteger -> long long long_BigLog = bigInteger.longValue(); System.out.println("BigInteger -> long : " + long_BigLog); // BigInteger -> float float float_BigFloat = bigInteger.floatValue(); System.out.println("BigInteger -> float : " + float_BigFloat); // BigInteger -> double double double_BigDouble = bigInteger.doubleValue(); System.out.println("BigInteger -> double : " + double_BigDouble); // BigInteger -> String String string_BigString = bigInteger.toString(); System.out.println("BigInteger -> String : " + string_BigString); } } class BigIntegerDeclaration { public void bigInteger() { // 문자열로 생성 BigInteger strBigInteger = new BigInteger("111111111111111111111"); System.out.println("문열로 선언 : " + strBigInteger); // 숫자로 생성 BigInteger numBigInteger = BigInteger.valueOf(222222222); System.out.println("숫자로 선언 : " + numBigInteger); // n진수로 생성 BigInteger nBigInteger1 = new BigInteger("FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF", 16); // 16진수 System.out.println("16진수로 선언 : " + nBigInteger1); BigInteger nBigInteger2 = new BigInteger("00010010010010001111", 2); System.out.println("2진수로 선언 : " + nBigInteger2); } } /* 출력 -----------------BigInteger 연산----------------- 덧셈 BigInteger.add : 222222222222 뺄셈 BigInteger.subtract : 0 곱셈 BigInteger.multiply : 12345679012320987654321 나눗셈 BigInteger.divide : 1 나머지 BigInteger.remainder : 0 */
4. BigInteger 비트 연산
- BigInteger는 큰 숫자를 다루는 대신 성능이 떨어집니다.
- 성능을 향상시키기 위해 비트단위로 연산하는 메서드들을 제공합니다.
-
메서드 설명 int bitCount() 2진수로 표현했을 때, 1의 개수(음수는 0의 개수)를 반환합니다. int bigLength() 2진수로 표현했을 때, 값을 표현하는데 필요한 bit 수를 반환합니다. boolean testBit(int n) 우측에서 n + 1 번째 비트가 1이면 true, 0이면 false를 반환합니다. BigInteger setBit(int n) 우측에서 n + 1 번째 비트를 1로 변경합니다. BigInteger clearBit(int n) 우측에서 n + 1 번째 비트를 0으로 변경합니다. BigInteger flipBit(int n) 우측에서 n + 1 번째 비트를 전환합니다. (1 -> 0, 0 -> 1) - BigInteger 타입의 숫자가 정수가 짝수인지 홀수인지 확인하는 방법으로, 제일 오른쪽 비트가 0일 것이므로 testBit(0)으로 마지막 비트를 확인하는 식으로 응용이 가능합니다.
- 또한 비트끼리 and, or, xor, not 연산이 가능합니다.
- 사용 예시
더보기
import java.math.BigInteger; public class BigIntegerBigDecimal { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("\n-----------------BigInteger 비트 연산-----------------"); BigIntegerBitCalculation bigIntegerBitCalculation = new BigIntegerBitCalculation(); bigIntegerBitCalculation.bigInteger(); } } class BigIntegerBitCalculation { public void bigInteger() { BigInteger bigInteger = new BigInteger("1018"); // 2진수로 표현하면 : 1111111010(2) int bitCount = bigInteger.bitCount(); System.out.println("BitCount : " + bitCount); // 1의 갯수 : 8 int bitLength = bigInteger.bitLength(); System.out.println("BitLength : " + bitLength); // 비트 수 : 10 boolean testBit3 = bigInteger.testBit(3 ); System.out.println("testBit : " + testBit3); // true BigInteger setBit12 = bigInteger.setBit(12); System.out.println("setBit : " + setBit12); // 우측에서 13번째 비트를 1로 변경 → 1001111111010(2) → 5114 BigInteger clearBit3 = bigInteger.clearBit(3); System.out.println("clearBit : " + clearBit3); // 1111110010(2) → 1010 BigInteger flipBit0 = bigInteger.flipBit(0); System.out.println("flipBit : " + flipBit0); // 1111111011(2) → 1019 BigInteger i = new BigInteger("17"); // 2진수 : 10001(2) BigInteger j = new BigInteger("7"); // 2진수 : 111(2) BigInteger and = i.and(j); System.out.println("and : " + and); // 10001(2) & 111(2) = 00001(2) → 1(10) BigInteger or = i.or(j); System.out.println("or : " + or); // 23 BigInteger xor = i.xor(j); System.out.println("xor : " + xor); // 22 BigInteger not = j.not(); System.out.println("not : " + not); // -8 BigInteger andNot = i.andNot(j); System.out.println("andNot : " + andNot); // 16 BigInteger shiftLeft = i.shiftLeft(1); System.out.println("shiftLeft : " + shiftLeft); // 34 BigInteger shiftRight = i.shiftRight(1); System.out.println("shiftRight : " + shiftRight); // 8 } } /* 출력 -----------------BigInteger 비트 연산----------------- BitCount : 8 BitLength : 10 testBit : true setBit : 5114 clearBit : 1010 flipBit : 1019 and : 1 or : 23 xor : 22 not : -8 andNot : 16 shiftLeft : 34 shiftRight : 8 */
5. BigInteger 숫자 비교
- BigInteger의 값을 비교할 때는 compareTo 메서드를 사용합니다.
- 사용 예시
더보기
import java.math.BigInteger; public class BigIntegerBigDecimal { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("\n-----------------BigInteger 숫자 비교-----------------"); BigIntegerComparison bigIntegerComparison = new BigIntegerComparison(); bigIntegerComparison.bigInteger(); } } class BigIntegerComparison { public void bigInteger() { BigInteger bigInteger1 = new BigInteger("1000"); BigInteger bigInteger2 = new BigInteger("10000"); int bigIntegerCompareTo = bigInteger1.compareTo(bigInteger2); System.out.println("compareTo : " + bigIntegerCompareTo); } } /* 출력 -----------------BigInteger 숫자 비교----------------- compareTo : -1 */
6. BigInteger 상수
- 자주 사용되는 숫자 0, 1, 2, 10은 BigInteger.ZERO, BigInteger.ONE, BigInteger.TWO, BigInteger.TEN으로 클래스 상수로서 제공됩니다.
- 이런 상수가 제공되는 이유는, BigInteger 연산에 있어 편리함을 제공하기 위해서입니다.
- 사용 예시
더보기
import java.math.BigInteger; public class BigIntegerBigDecimal { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("\n-----------------BigInteger 상수-----------------"); BigIntegerConstant bigIntegerConstant = new BigIntegerConstant(); bigIntegerConstant.bigInteger(); } } class BigIntegerConstant { public void bigInteger() { System.out.println("BigInteger.ZERO : " + BigInteger.ZERO); System.out.println("BigInteger.ONE : " + BigInteger.ONE); System.out.println("BigInteger.TWO : " + BigInteger.TWO); System.out.println("BigInteger.TEN : " + BigInteger.TEN); // 숫자 10을 valueOf를 통해 BigInteger 클래스로 초기화하고 연산을 해야되지만, System.out.println( "BigInteger.valueOf를 이용한 덧셈 : " + new BigInteger("20").add(BigInteger.valueOf(10))); // 30 // 자주 사용되는 숫자일 경우 BigInteger 상수로 바로 계산이 가능하다는 장점이 있다 System.out.println( "BigInteger.TEN을 이용한 덧셈 : " + new BigInteger("20").add(BigInteger.TEN)); // 30 } } /* 출력 -----------------BigInteger 상수----------------- BigInteger.ZERO : 0 BigInteger.ONE : 1 BigInteger.TWO : 2 BigInteger.TEN : 10 BigInteger.valueOf를 이용한 덧셈 : 30 BigInteger.TEN을 이용한 덧셈 : 30 */
BigDecimal 자료형
BigDecimal 사용되는 경우
| Type | 범위 |
| float | 1.4E-45 ~ 3.4028235E38 |
| double | 4.9E-324 ~ 1.7976931348623157E308 |
- 부동 소수점을 이용해 실수 넘버를 저장하는 타입인 float과 double은 소수점의 정밀도가 완벽하지 않는 특징을 지니고 있습니다.
- 그래서 소수점 이하의 수를 다룰 때 사칙연산 시 정확한 값을 출력하지 않게 됩니다.
이유는 내부적으로 수를 저장할 때 이진수의 근사치를 저장하기 때문입니다. -
double value1 = 12.23; double value2 = 34.45; // 기대값 : 46.68 System.out.println(value1 + value2); // 46.68000000000001 - 위 코드에서 12.23과 23.45를 더했을 때 결과는 46.68을 예상하지만, 실제로는 46.68000000000001이 출력되는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
- 수의 크기로서 보면 아주 작은 근사한 차이지만, 금융 관련 프로그램에서는 이 오차가 큰 영향을 미칠 수 있기 때문에 주의해야 합니다.
- 이럴 때 사용할 수 있는 BigDecimal에 대해서 알아보겠습니다.
- BigDecimal은 float, double보다 느리지만 정밀한 결과를 보장합니다.
BigDecimal 사용법
1. BigDecimal 선언
- BigDecimal 클래스는 java.math 패키지 안에 포함되어 있습니다.
- BigDecimal은 BigInteger와 매우 비슷한 형태임을 확인할 수 있습니다. 차이점은 정수냐 실수냐의 차이라고 할 수 있습니다.
- double, int, long 타입으로도 생성이 가능하지만, double의 정밀도의 한계가 있어 사용하는 클래스이므로 double 타입으로 생성할 경우 오차 발생 가능성이 존재합니다. 그래서 BigDecimal 역시 BigInteger처럼 보통 문자열로 생성합니다.
- 사용 예시
더보기
import java.math.BigDecimal; import java.math.BigInteger; public class BigIntegerBigDecimal { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("\n-----------------BigDecimal 선언-----------------"); BigDecimalDeclaration bigDecimalDeclaration = new BigDecimalDeclaration(); bigDecimalDeclaration.bigDecimal(); } } class BigDecimalDeclaration { public void bigDecimal() { // 문자열로 생성 BigDecimal strBigDecimal = new BigDecimal("123.456"); System.out.println("문자열로 선언 : " + strBigDecimal); // double 타입으로 생성 (오차가 발생할 수 있습니다.) - 비추천 BigDecimal doubleBigDecimal = new BigDecimal(123.456); System.out.println("double로 선언 : " + doubleBigDecimal); // valueOf 생성 BigDecimal valueOfBigDecimal = BigDecimal.valueOf(123.456); System.out.println("valueOf로 선언 : " + valueOfBigDecimal); // 소수점 아래자리수 지정 BigDecimal valueOfBigDecimal2 = BigDecimal.valueOf(123456L, 3); System.out.println("소수점 아래자리수 지정 : " + valueOfBigDecimal2); } } /* 출력 -----------------BigDecimal 선언----------------- 문자열로 선언 : 123.456 double로 선언 : 123.4560000000000030695446184836328029632568359375 valueOf로 선언 : 123.456 소수점 아래자리수 지정 : 123.456 */
2. BigDecimal 형 변환
- 사용 예시
더보기
import java.math.BigDecimal; import java.math.BigInteger; public class BigIntegerBigDecimal { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("\n-----------------BigDecimal 형변환-----------------"); BigDecimalTypeConversion bigDecimalTypeConversion = new BigDecimalTypeConversion(); bigDecimalTypeConversion.bigDecimal(); } } class BigDecimalTypeConversion { public void bigDecimal() { // double -> BigDecimal BigDecimal bigDecimal = BigDecimal.valueOf(123.456789); System.out.println("int -> BigDecimal : " + bigDecimal); // BigDecimal -> int int int_bigDecimal = bigDecimal.intValue(); System.out.println("BigDecimal -> int : " + int_bigDecimal); // BigDecimal -> long long long_bigDecimal = bigDecimal.longValue(); System.out.println("BigDecimal -> long : " + long_bigDecimal); // BigDecimal -> float float float_bigDecimal = bigDecimal.floatValue(); System.out.println("BigDecimal -> float : " + float_bigDecimal); // BigDecimal -> double double double_bigDecimal = bigDecimal.doubleValue(); System.out.println("BigDecimal -> double : " + double_bigDecimal); // BigDecimal -> String String String_bigDecimal = bigDecimal.toString(); System.out.println("BigDecimal -> String : " + String_bigDecimal); } } /* 출력 -----------------BigDecimal 형변환----------------- int -> BigDecimal : 123.456789 BigDecimal -> int : 123 BigDecimal -> long : 123 BigDecimal -> float : 123.45679 BigDecimal -> double : 123.456789 BigDecimal -> String : 123.456789 */
3, BigDecimal 연산
-
메서드 설명 BigDecimal add(BigDecimal val) 덧셈 (this + val) BigDecimal subtract(BigDecimal val) 뺄셈 (this + val) BigDecimal multiply(BigDecimal val) 곱셈 (this * vall) BigDecimal divide(BigDecimal val) 나눗셈 (this / vall) BigDecimal remainder(BigDecimal val) 나머지 (this % vall) - 사용 예시
더보기
import java.math.BigDecimal; import java.math.BigInteger; public class BigIntegerBigDecimal { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("\n-----------------BigDecimal 연산-----------------"); BigDecimalCalculation bigDecimalCalculation = new BigDecimalCalculation(); bigDecimalCalculation.bigDecimal(); } } class BigDecimalCalculation { public void bigDecimal() { BigDecimal bigNumber1 = new BigDecimal("100.12345"); BigDecimal bigNumber2 = new BigDecimal("10"); System.out.println("덧셈 BigDecimal.add :" +bigNumber1.add(bigNumber2)); // 덧셈(+) :110000.12345 System.out.println("뺄셈 BigDecimal.subtract :" +bigNumber1.subtract(bigNumber2)); // 뺄셈(-) :90000.12345 System.out.println("곱셈 BigDecimal.multiply :" +bigNumber1.multiply(bigNumber2)); // 곱셈(*) :1000001234.50000 System.out.println("나눗셈 BigDecimal.divide :" +bigNumber1.divide(bigNumber2)); // 나눗셈(/) :10.000012345 System.out.println("나머지 BigDecimal.remainder :" +bigNumber1.remainder(bigNumber2)); // 나머지(%) :0.12345 } } /* 출력 -----------------BigDecimal 연산----------------- 덧셈 BigDecimal.add :110.12345 뺄셈 BigDecimal.subtract :90.12345 곱셈 BigDecimal.multiply :1001.23450 나눗셈 BigDecimal.divide :10.012345 나머지 BigDecimal.remainder :0.12345 */
4. BigDecimal 숫자 비교
- 사용 예시
더보기
import java.math.BigDecimal; import java.math.BigInteger; import java.math.RoundingMode; import java.util.Scanner; public class BigIntegerBigDecimal { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("\n-----------------BigDecimal 숫자 비교-----------------"); BigDecimalComparison bigDecimalComparison = new BigDecimalComparison(); bigDecimalComparison.bigDecimal(); } } class BigDecimalComparison { public void bigDecimal() { BigDecimal bigNumber1 = new BigDecimal("123.45"); BigDecimal bigNumber2 = new BigDecimal("123.456"); int compare = bigNumber1.compareTo(bigNumber2); //-1 System.out.println(compare); } } /* 출력 -----------------BigDecimal 숫자 비교----------------- -1 */
5. BigDecimal 정밀도 값
- BigDecimal은 실수 자료형이기 때문에 정밀도, 스케일, 부호 같은 속성을 추출하는 메서드가 존재합니다.
- 사용 예시
더보기
import java.math.BigDecimal; import java.math.BigInteger; import java.math.RoundingMode; import java.util.Scanner; public class BigIntegerBigDecimal { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("\n-----------------BigDecimal 정밀도 값-----------------"); BigDecimalPrecision bigDecimalPrecision = new BigDecimalPrecision(); bigDecimalPrecision.bigDecimal(); } } class BigDecimalPrecision { public void bigDecimal() { BigDecimal bigDecimal = new BigDecimal("-12345.6789"); System.out.println("정밀도 bigDecimal.precision : " + bigDecimal.precision()); // 정밀도 : 9 System.out.println("지수값(스케일) bigDecimal.scale : " + bigDecimal.scale()); // 지수값(스케일) : 4 System.out.println("부호 bigDecimal.signum : " + bigDecimal.signum()); // 부호 : -1(음수) } } /* 출력 -----------------BigDecimal 정밀도 값----------------- 정밀도 bigDecimal.precision : 9 지수값(스케일) bigDecimal.scale : 4 부호 bigDecimal.signum : -1 */
6. BigDecimal 자수(E) 제거
- 가끔 커다란 실수 값을 다룰 때, 지수 (E) 부호가 붙어 있는 값을 다룰 때가 있습니다.
- 예를들면 2000000을 2.0E7로 표현하는데 이를 그대로 연산에 이용할 수 없어서 수동 숫자 변환이 필요합니다.
- 해결법으로 Double로 파싱한 뒤, new BigDecimal 객체를 생성해주면 됩니다.
- 사용 예시
더보기
import java.math.BigDecimal; import java.math.BigInteger; import java.math.RoundingMode; import java.util.Scanner; public class BigIntegerBigDecimal { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("\n-----------------BigDecimal 지수 제거-----------------"); BigDecimalRemoveExponent bigDecimalRemoveExponent = new BigDecimalRemoveExponent(); bigDecimalRemoveExponent.bigDecimal(); } } class BigDecimalRemoveExponent { public void bigDecimal() { String str = "1.0E7"; BigDecimal exponentBigDecimal = new BigDecimal(str); // 지수 붙음 System.out.println("지수 붙은 BigDecimal : " + exponentBigDecimal); // 1.0E+7 BigDecimal removeExponentBigDecimal = new BigDecimal(Double.parseDouble(str)); // 지수 제거 System.out.println("지수 제거된 BigDecimal : " + removeExponentBigDecimal); // 10000000 } } /* 출력 -----------------BigDecimal 지수 제거----------------- 지수 붙은 BigDecimal : 1.0E+7 지수 제거된 BigDecimal : 10000000 */
BigDecimal 반올림 정책
1. java.lang.ArithmeticException
- BigDecimal 타입의 실순는 divide 메서드를 사용하면 나눗셈 연산이 가능합니다.
- 하지만 주의해야 할 점은, 실수 나눗셈의 결과가 정확하게 나누어 몫이 떨어지지 않는 수의 경우 java.lang.ArithmeticException 예외가 발생한다는 점입니다.
- 예시
더보기
import java.math.BigDecimal; import java.math.BigInteger; import java.math.RoundingMode; import java.util.Scanner; public class BigIntegerBigDecimal { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("\n-----------------BigDecimal Exception 예시-----------------"); BigDecimalException bigDecimalException = new BigDecimalException(); bigDecimalException.bigDecimal(); } } class BigDecimalException { public void bigDecimal() { BigDecimal bigDecimal1 = new BigDecimal("11"); BigDecimal bigDecimal2 = BigDecimal.valueOf(3); // System.out.println(bigDecimal1.divide(bigDecimal2)); System.out.println("ArithmeticException 발생"); } } /* 출력 -----------------BigDecimal Exception 예시----------------- ArithmeticException 발생 */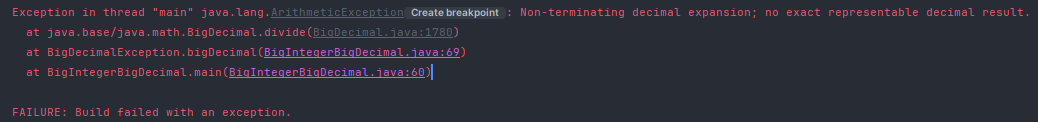
- 따라서 BigDecimal의 나눗셈은 보다 정확한 계산을 위해서 소수점 몇 번째까지, 어떻게 처리할 것인지 지정해줘야 합니다.
- 해결 방법
더보기
import java.math.BigDecimal; import java.math.BigInteger; import java.math.RoundingMode; import java.util.Scanner; public class BigIntegerBigDecimal { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("\n-----------------BigDecimal Exception 예시-----------------"); BigDecimalException bigDecimalException = new BigDecimalException(); bigDecimalException.bigDecimal(); } } class BigDecimalExceptionResult { public void bigDecimal() { BigDecimal bigDecimal1 = new BigDecimal("11"); BigDecimal bigDecimal2 = BigDecimal.valueOf(3); System.out.println("ArithmeticException Result"); // divide()의 2번째 파라미터는 N 번째 자리까지 표현할 것인가를 뜻하고, 3번째 파라미터는 반올림 정책 처리 방식이다. // 소수점 3번째 자리에서 반올림하여 2번째 자리까지 표기한다. System.out.println(bigDecimal1.divide(bigDecimal2, 2, RoundingMode.HALF_EVEN)); } } /* 출력 -----------------BigDecimal Exception 해결 방법----------------- ArithmeticException Result 3.67 */
2. BigDecimal - RoundingMode
- 위 코드에서 반올림 처리 방법으로 RoundingMode.HALF_EVEN이라는 상수를 사용했는데, 이것이 반올림 정책입니다.
- 자바에서는 BigDecimal 클래스에 다양한 소수점 처리 방식을 제공하고 있습니다.
- 아무래도 부동 소수점의 실수를 다루는데 있어 부정확한 실수 연산값을 보완하기 위해 반올림을 명확히 지정할 필요가 있기 때문에 자바 프로그래밍에서 지원하는 것입니다.
-
상수 설명 RoundingMode.CEILING 올림 RoundingMode.FLOOR 내림 RoundingMode.UP 양수일 때, 올림, 음수일 때 내림 RoundingMode.DOWN up과 반대로 양수일 때 내림, 음수일 떄 올림 RoundingMode.HALF_UP 반올림 (5이상 올림, 5미만 버림) RoundingMode.HALF_EVEN 반올림 (반올림 자리의 값이 짝수면 HALF_DOWN, 홀수면 HALF_UP RoundingMode.HALF_DOWN 반올림 (6이상 올림, 6미만 버림) RoundingMode.UNNECESSARY 나눗셈 결과가 정확히 떨어지는 수가 아니면, ArithmeticException 발생 - 사용 방법으로 divide() 메서드
첫 번째 인자로 실수 값,
두 번째 인자로 소수점 자리수,
세 번째 인자로 반올림 정책을 지정합니다.
* 인수 3개를 다 작성하지 않아도 됩니다. - 사용 예시
더보기
import java.math.BigDecimal; import java.math.BigInteger; import java.math.RoundingMode; import java.util.Scanner; public class BigIntegerBigDecimal { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("\n-----------------BigDecimal 반올림 정책-----------------"); BigDecimalRoundingMode bigDecimalRoundingMode = new BigDecimalRoundingMode(); bigDecimalRoundingMode.bigDecimal(); } } class BigDecimalRoundingMode { public void bigDecimal() { BigDecimal bigDecimal1 = new BigDecimal("10"); BigDecimal bigDecimal2 = new BigDecimal("3"); System.out.println("bigDecimal1.divide(bigDecimal2) -> ArithmeticException"); System.out.println("반올림 정책으로 나누어 떨어집니다."); System.out.println("실수 값과 반올림 정책을 이용 : " + bigDecimal1.divide(bigDecimal2, RoundingMode.HALF_EVEN)); // 반올림 자리값을 명시 System.out.println("실수 값, 소수점 자리, 반올림 정책 이용 : " + bigDecimal1.divide(bigDecimal2, 6, RoundingMode.HALF_EVEN)); } } /* 출력 -----------------BigDecimal 반올림 정책----------------- bigDecimal1.divide(bigDecimal2) -> ArithmeticException 반올림 정책으로 나누어 떨어집니다. 실수 값과 반올림 정책을 이용 : 3 실수 값, 소수점 자리, 반올림 정책 이용 : 3.333333 */ - 혹은 연산 값이 아닌 고정된 실수에 대해서도 setScale() 메서드를 통해 반올림 정책을 지정할 수 있습니다.
- 사용 예시
더보기
import java.math.BigDecimal; import java.math.BigInteger; import java.math.RoundingMode; import java.util.Scanner; public class BigIntegerBigDecimal { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("\n-----------------BigDecimal setScale 이용-----------------"); BigDecimalSetScale bigDecimalSetScale = new BigDecimalSetScale(); bigDecimalSetScale.bigDecimal(); } } class BigDecimalSetScale { public void bigDecimal() { System.out.println("setScale을 이용하여 소수점 첫 번째까지 표현, 두번째 자리에서 반올림 지정 : " + BigDecimal.valueOf(12.35).setScale(1, RoundingMode.HALF_UP)); System.out.println("setScale을 이용하여 소수점 이하 모두 제거하고 올림 지정 : " + BigDecimal.valueOf(12.34).setScale(0, RoundingMode.CEILING)); System.out.println("setScale을 이용하여 음수인 경우는 특정 자릿수 이하 제거 지정 : " + BigDecimal.valueOf(-12.34).setScale(1, RoundingMode.CEILING)); System.out.println("setScale을 이용하여 특정 자릿수 이하 버림 지정 : " + new BigDecimal("12.37").setScale(1, RoundingMode.FLOOR)); Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("입력 값을 setScale을 이용하여 소수점 첫 번째까지 표현, 두번째 자리에서 반올림 지정 : " + new BigDecimal(in.nextLine()).setScale(1, RoundingMode.HALF_UP)); } } /* 출력 -----------------BigDecimal setScale 이용----------------- setScale을 이용하여 소수점 첫 번째까지 표현, 두번째 자리에서 반올림 지정 : 12.4 setScale을 이용하여 소수점 이하 모두 제거하고 올림 지정 : 13 setScale을 이용하여 음수인 경우는 특정 자릿수 이하 제거 지정 : -12.3 setScale을 이용하여 특정 자릿수 이하 버림 지정 : 12.3 12.35 입력 값을 setScale을 이용하여 소수점 첫 번째까지 표현, 두번째 자리에서 반올림 지정 : 12.4 */
3. BigDecimal - MathContext
- 반올림 동작을 제어하는데 RoundingMode와 같이 MathContext 클래스도 존재합니다.
- MathContext는 반올림 모드와 정밀도 (precision)를 하나로 묶어놓은 것일 뿐인 클래스입니다.
-
상수 설명 MathContext.DECIMAL32 7자리 정밀도 및 HALF_EVEN의 반올림 모드 MathContext.DECIMAL64 16자리 정밀도 및 HALF_EVEN의 반올림 모드 MathContext.DECIMAL128 34자리 정밀도 및 HALF_EVEN의 반올림 모드 MathContext.UNLIMTED 무제한 정밀 산술 - 사용 예시
더보기
import java.math.BigDecimal; import java.math.BigInteger; import java.math.MathContext; import java.math.RoundingMode; import java.util.Scanner; public class BigIntegerBigDecimal { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("\n-----------------BigDecimal MathContext 이용-----------------"); BigDecimalMathContext bigDecimalMathContext = new BigDecimalMathContext(); bigDecimalMathContext.bigDecimal(); } } class BigDecimalMathContext { public void bigDecimal() { BigDecimal bigDecimal1 = new BigDecimal("10"); BigDecimal bigDecimal2 = new BigDecimal("3"); System.out.println("MathContext을 이용하여 전체 자리수를 7개로 제한하고 HALF_EVEN 반올림을 적용 : " + bigDecimal1.divide(bigDecimal2, MathContext.DECIMAL32)); System.out.println("MathContext을 이용하여 전체 자리수를 16개로 제한하고 HALF_EVEN 반올림을 적용 : " + bigDecimal1.divide(bigDecimal2, MathContext.DECIMAL64)); System.out.println("MathContext을 이용하여 전체 자리수를 34개로 제한하고 HALF_EVEN 반올림을 적용한 : " + bigDecimal1.divide(bigDecimal2, MathContext.DECIMAL128)); System.out.println( "MathContext을 // 전체 자리수를 제한하지 않게 적용 -> ArithmeticException 예외 발생 : " + "bigDecimal1.divide(bigDecimal2, MathContext.UNLIMITED) "); } } /* 출력 -----------------BigDecimal MathContext 이용----------------- MathContext을 이용하여 전체 자리수를 7개로 제한하고 HALF_EVEN 반올림을 적용 : 3.333333 MathContext을 이용하여 전체 자리수를 16개로 제한하고 HALF_EVEN 반올림을 적용 : 3.333333333333333 MathContext을 이용하여 전체 자리수를 34개로 제한하고 HALF_EVEN 반올림을 적용한 : 3.333333333333333333333333333333333 MathContext을 // 전체 자리수를 제한하지 않게 적용 -> ArithmeticException 예외 발생 : bigDecimal1.divide(bigDecimal2, MathContext.UNLIMITED) */
최종 코드
더보기
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.math.MathContext;
import java.math.RoundingMode;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class BigIntegerBigDecimal {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("\n~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~BIG INTEGER~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~");
System.out.println("\n-----------------BigInteger 선언-----------------");
BigIntegerDeclaration bigIntegerDeclaration = new BigIntegerDeclaration();
bigIntegerDeclaration.bigInteger();
System.out.println("\n-----------------BigInteger 형 변환-----------------");
BigIntegerTypeConversion bigIntegerTypeConversion = new BigIntegerTypeConversion();
bigIntegerTypeConversion.bigInteger();
System.out.println("\n-----------------BigInteger 연산-----------------");
BigIntegerCalculation bigIntegerCalculation = new BigIntegerCalculation();
bigIntegerCalculation.binInteger();
System.out.println("\n-----------------BigInteger 비트 연산-----------------");
BigIntegerBitCalculation bigIntegerBitCalculation = new BigIntegerBitCalculation();
bigIntegerBitCalculation.bigInteger();
System.out.println("\n-----------------BigInteger 숫자 비교-----------------");
BigIntegerComparison bigIntegerComparison = new BigIntegerComparison();
bigIntegerComparison.bigInteger();
System.out.println("\n-----------------BigInteger 상수-----------------");
BigIntegerConstant bigIntegerConstant = new BigIntegerConstant();
bigIntegerConstant.bigInteger();
System.out.println("\n~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~BIG DECIMAL~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~");
System.out.println("\n-----------------BigDecimal 선언-----------------");
BigDecimalDeclaration bigDecimalDeclaration = new BigDecimalDeclaration();
bigDecimalDeclaration.bigDecimal();
System.out.println("\n-----------------BigDecimal 형변환-----------------");
BigDecimalTypeConversion bigDecimalTypeConversion = new BigDecimalTypeConversion();
bigDecimalTypeConversion.bigDecimal();
System.out.println("\n-----------------BigDecimal 연산-----------------");
BigDecimalCalculation bigDecimalCalculation = new BigDecimalCalculation();
bigDecimalCalculation.bigDecimal();
System.out.println("\n-----------------BigDecimal 숫자 비교-----------------");
BigDecimalComparison bigDecimalComparison = new BigDecimalComparison();
bigDecimalComparison.bigDecimal();
System.out.println("\n-----------------BigDecimal 정밀도 값-----------------");
BigDecimalPrecision bigDecimalPrecision = new BigDecimalPrecision();
bigDecimalPrecision.bigDecimal();
System.out.println("\n-----------------BigDecimal 지수 제거-----------------");
BigDecimalRemoveExponent bigDecimalRemoveExponent = new BigDecimalRemoveExponent();
bigDecimalRemoveExponent.bigDecimal();
System.out.println("\n-----------------BigDecimal Exception 예시-----------------");
BigDecimalException bigDecimalException = new BigDecimalException();
bigDecimalException.bigDecimal();
System.out.println("\n-----------------BigDecimal Exception 해결 방법-----------------");
BigDecimalExceptionResult bigDecimalExceptionResult = new BigDecimalExceptionResult();
bigDecimalExceptionResult.bigDecimal();
System.out.println("\n-----------------BigDecimal 반올림 정책-----------------");
BigDecimalRoundingMode bigDecimalRoundingMode = new BigDecimalRoundingMode();
bigDecimalRoundingMode.bigDecimal();
System.out.println("\n-----------------BigDecimal setScale 이용-----------------");
BigDecimalSetScale bigDecimalSetScale = new BigDecimalSetScale();
bigDecimalSetScale.bigDecimal();
System.out.println("\n-----------------BigDecimal MathContext 이용-----------------");
BigDecimalMathContext bigDecimalMathContext = new BigDecimalMathContext();
bigDecimalMathContext.bigDecimal();
}
}
class BigDecimalMathContext {
public void bigDecimal() {
BigDecimal bigDecimal1 = new BigDecimal("10");
BigDecimal bigDecimal2 = new BigDecimal("3");
System.out.println("MathContext을 이용하여 전체 자리수를 7개로 제한하고 HALF_EVEN 반올림을 적용 : " +
bigDecimal1.divide(bigDecimal2, MathContext.DECIMAL32));
System.out.println("MathContext을 이용하여 전체 자리수를 16개로 제한하고 HALF_EVEN 반올림을 적용 : " +
bigDecimal1.divide(bigDecimal2, MathContext.DECIMAL64));
System.out.println("MathContext을 이용하여 전체 자리수를 34개로 제한하고 HALF_EVEN 반올림을 적용한 : " +
bigDecimal1.divide(bigDecimal2, MathContext.DECIMAL128));
System.out.println(
"MathContext을 // 전체 자리수를 제한하지 않게 적용 -> ArithmeticException 예외 발생 : "
+ "bigDecimal1.divide(bigDecimal2, MathContext.UNLIMITED) ");
}
}
class BigDecimalSetScale {
public void bigDecimal() {
System.out.println("setScale을 이용하여 소수점 첫 번째까지 표현, 두번째 자리에서 반올림 지정 : " +
BigDecimal.valueOf(12.35).setScale(1, RoundingMode.HALF_UP));
System.out.println("setScale을 이용하여 소수점 이하 모두 제거하고 올림 지정 : " +
BigDecimal.valueOf(12.34).setScale(0, RoundingMode.CEILING));
System.out.println("setScale을 이용하여 음수인 경우는 특정 자릿수 이하 제거 지정 : " +
BigDecimal.valueOf(-12.34).setScale(1, RoundingMode.CEILING));
System.out.println("setScale을 이용하여 특정 자릿수 이하 버림 지정 : " +
new BigDecimal("12.37").setScale(1, RoundingMode.FLOOR));
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("입력 값을 setScale을 이용하여 소수점 첫 번째까지 표현, 두번째 자리에서 반올림 지정 : " +
new BigDecimal(in.nextLine()).setScale(1, RoundingMode.HALF_UP));
}
}
class BigDecimalRoundingMode {
public void bigDecimal() {
BigDecimal bigDecimal1 = new BigDecimal("10");
BigDecimal bigDecimal2 = new BigDecimal("3");
System.out.println("bigDecimal1.divide(bigDecimal2) -> ArithmeticException");
System.out.println("반올림 정책으로 나누어 떨어집니다.");
System.out.println("실수 값과 반올림 정책을 이용 : " +
bigDecimal1.divide(bigDecimal2, RoundingMode.HALF_EVEN));
// 반올림 자리값을 명시
System.out.println("실수 값, 소수점 자리, 반올림 정책 이용 : " +
bigDecimal1.divide(bigDecimal2, 6, RoundingMode.HALF_EVEN));
}
}
class BigDecimalExceptionResult {
public void bigDecimal() {
BigDecimal bigDecimal1 = new BigDecimal("11");
BigDecimal bigDecimal2 = BigDecimal.valueOf(3);
System.out.println("ArithmeticException Result");
// divide()의 2번째 파라미터는 N 번째 자리까지 표현할 것인가를 뜻하고, 3번째 파라미터는 반올림 정책 처리 방식이다.
// 소수점 3번째 자리에서 반올림하여 2번째 자리까지 표기한다.
System.out.println(bigDecimal1.divide(bigDecimal2, 2, RoundingMode.HALF_EVEN));
}
}
class BigDecimalException {
public void bigDecimal() {
BigDecimal bigDecimal1 = new BigDecimal("11");
BigDecimal bigDecimal2 = BigDecimal.valueOf(3);
// System.out.println(bigDecimal1.divide(bigDecimal2));
System.out.println("ArithmeticException 발생");
}
}
class BigDecimalRemoveExponent {
public void bigDecimal() {
String str = "1.0E7";
BigDecimal exponentBigDecimal = new BigDecimal(str); // 지수 붙음
System.out.println("지수 붙은 BigDecimal : " + exponentBigDecimal); // 1.0E+7
BigDecimal removeExponentBigDecimal = new BigDecimal(Double.parseDouble(str)); // 지수 제거
System.out.println("지수 제거된 BigDecimal : " + removeExponentBigDecimal); // 10000000
}
}
class BigDecimalPrecision {
public void bigDecimal() {
BigDecimal bigDecimal = new BigDecimal("-12345.6789");
System.out.println("정밀도 bigDecimal.precision : " + bigDecimal.precision()); // 정밀도 : 9
System.out.println("지수값(스케일) bigDecimal.scale : " + bigDecimal.scale()); // 지수값(스케일) : 4
System.out.println("부호 bigDecimal.signum : " + bigDecimal.signum()); // 부호 : -1(음수)
}
}
class BigDecimalComparison {
public void bigDecimal() {
BigDecimal bigNumber1 = new BigDecimal("123.45");
BigDecimal bigNumber2 = new BigDecimal("123.456");
int compare = bigNumber1.compareTo(bigNumber2); //-1
System.out.println(compare);
}
}
class BigDecimalCalculation {
public void bigDecimal() {
BigDecimal bigNumber1 = new BigDecimal("100.12345");
BigDecimal bigNumber2 = new BigDecimal("10");
System.out.println("덧셈 BigDecimal.add :" +bigNumber1.add(bigNumber2)); // 덧셈(+) :110000.12345
System.out.println("뺄셈 BigDecimal.subtract :" +bigNumber1.subtract(bigNumber2)); // 뺄셈(-) :90000.12345
System.out.println("곱셈 BigDecimal.multiply :" +bigNumber1.multiply(bigNumber2)); // 곱셈(*) :1000001234.50000
System.out.println("나눗셈 BigDecimal.divide :" +bigNumber1.divide(bigNumber2)); // 나눗셈(/) :10.000012345
System.out.println("나머지 BigDecimal.remainder :" +bigNumber1.remainder(bigNumber2)); // 나머지(%) :0.12345
}
}
class BigDecimalTypeConversion {
public void bigDecimal() {
// double -> BigDecimal
BigDecimal bigDecimal = BigDecimal.valueOf(123.456789);
System.out.println("int -> BigDecimal : " + bigDecimal);
// BigDecimal -> int
int int_bigDecimal = bigDecimal.intValue();
System.out.println("BigDecimal -> int : " + int_bigDecimal);
// BigDecimal -> long
long long_bigDecimal = bigDecimal.longValue();
System.out.println("BigDecimal -> long : " + long_bigDecimal);
// BigDecimal -> float
float float_bigDecimal = bigDecimal.floatValue();
System.out.println("BigDecimal -> float : " + float_bigDecimal);
// BigDecimal -> double
double double_bigDecimal = bigDecimal.doubleValue();
System.out.println("BigDecimal -> double : " + double_bigDecimal);
// BigDecimal -> String
String String_bigDecimal = bigDecimal.toString();
System.out.println("BigDecimal -> String : " + String_bigDecimal);
}
}
class BigDecimalDeclaration {
public void bigDecimal() {
// 문자열로 생성
BigDecimal strBigDecimal = new BigDecimal("123.456");
System.out.println("문자열로 선언 : " + strBigDecimal);
// double 타입으로 생성 (오차가 발생할 수 있습니다.) - 비추천
BigDecimal doubleBigDecimal = new BigDecimal(123.456);
System.out.println("double로 선언 : " + doubleBigDecimal);
// valueOf 생성
BigDecimal valueOfBigDecimal = BigDecimal.valueOf(123.456);
System.out.println("valueOf로 선언 : " + valueOfBigDecimal);
// 소수점 아래자리수 지정
BigDecimal valueOfBigDecimal2 = BigDecimal.valueOf(123456L, 3);
System.out.println("소수점 아래자리수 지정 : " + valueOfBigDecimal2);
}
}
class BigIntegerConstant {
public void bigInteger() {
System.out.println("BigInteger.ZERO : " + BigInteger.ZERO);
System.out.println("BigInteger.ONE : " + BigInteger.ONE);
System.out.println("BigInteger.TWO : " + BigInteger.TWO);
System.out.println("BigInteger.TEN : " + BigInteger.TEN);
// 숫자 10을 valueOf를 통해 BigInteger 클래스로 초기화하고 연산을 해야되지만,
System.out.println(
"BigInteger.valueOf를 이용한 덧셈 : " +
new BigInteger("20").add(BigInteger.valueOf(10))); // 30
// 자주 사용되는 숫자일 경우 BigInteger 상수로 바로 계산이 가능하다는 장점이 있다
System.out.println(
"BigInteger.TEN을 이용한 덧셈 : " +
new BigInteger("20").add(BigInteger.TEN)); // 30
}
}
class BigIntegerComparison {
public void bigInteger() {
BigInteger bigInteger1 = new BigInteger("1000");
BigInteger bigInteger2 = new BigInteger("10000");
int bigIntegerCompareTo = bigInteger1.compareTo(bigInteger2);
System.out.println("compareTo : " + bigIntegerCompareTo);
}
}
class BigIntegerBitCalculation {
public void bigInteger() {
BigInteger bigInteger = new BigInteger("1018"); // 2진수로 표현하면 : 1111111010(2)
int bitCount = bigInteger.bitCount();
System.out.println("BitCount : " + bitCount); // 1의 갯수 : 8
int bitLength = bigInteger.bitLength();
System.out.println("BitLength : " + bitLength); // 비트 수 : 10
boolean testBit3 = bigInteger.testBit(3 );
System.out.println("testBit : " + testBit3); // true
BigInteger setBit12 = bigInteger.setBit(12);
System.out.println("setBit : " + setBit12); // 우측에서 13번째 비트를 1로 변경 → 1001111111010(2) → 5114
BigInteger clearBit3 = bigInteger.clearBit(3);
System.out.println("clearBit : " + clearBit3); // 1111110010(2) → 1010
BigInteger flipBit0 = bigInteger.flipBit(0);
System.out.println("flipBit : " + flipBit0); // 1111111011(2) → 1019
BigInteger i = new BigInteger("17"); // 2진수 : 10001(2)
BigInteger j = new BigInteger("7"); // 2진수 : 111(2)
BigInteger and = i.and(j);
System.out.println("and : " + and); // 10001(2) & 111(2) = 00001(2) → 1(10)
BigInteger or = i.or(j);
System.out.println("or : " + or); // 23
BigInteger xor = i.xor(j);
System.out.println("xor : " + xor); // 22
BigInteger not = j.not();
System.out.println("not : " + not); // -8
BigInteger andNot = i.andNot(j);
System.out.println("andNot : " + andNot); // 16
BigInteger shiftLeft = i.shiftLeft(1);
System.out.println("shiftLeft : " + shiftLeft); // 34
BigInteger shiftRight = i.shiftRight(1);
System.out.println("shiftRight : " + shiftRight); // 8
}
}
class BigIntegerCalculation {
public void binInteger() {
BigInteger bigInteger = new BigInteger("111111111111");
BigInteger bigInteger1 = new BigInteger("111111111111");
System.out.println("덧셈 BigInteger.add : " + bigInteger.add(bigInteger1));
System.out.println("뺄셈 BigInteger.subtract : " + bigInteger.subtract(bigInteger1));
System.out.println("곱셈 BigInteger.multiply : " + bigInteger.multiply(bigInteger1));
System.out.println("나눗셈 BigInteger.divide : " + bigInteger.divide(bigInteger1));
System.out.println("나머지 BigInteger.remainder : " + bigInteger.remainder(bigInteger1));
}
}
class BigIntegerTypeConversion {
public void bigInteger() {
// int / long -> BigInteger
int num = 1000000000;
BigInteger bigInteger = BigInteger.valueOf(num);
System.out.println("int -> BigInteger : " + bigInteger);
// BigInteger -> int
int int_BigInt = bigInteger.intValue();
System.out.println("BigInteger -> int : " + int_BigInt);
// BigInteger -> long
long long_BigLog = bigInteger.longValue();
System.out.println("BigInteger -> long : " + long_BigLog);
// BigInteger -> float
float float_BigFloat = bigInteger.floatValue();
System.out.println("BigInteger -> float : " + float_BigFloat);
// BigInteger -> double
double double_BigDouble = bigInteger.doubleValue();
System.out.println("BigInteger -> double : " + double_BigDouble);
// BigInteger -> String
String string_BigString = bigInteger.toString();
System.out.println("BigInteger -> String : " + string_BigString);
}
}
class BigIntegerDeclaration {
public void bigInteger() {
// 문자열로 생성
BigInteger strBigInteger = new BigInteger("111111111111111111111");
System.out.println("문열로 선언 : " + strBigInteger);
// 숫자로 생성
BigInteger numBigInteger = BigInteger.valueOf(222222222);
System.out.println("숫자로 선언 : " + numBigInteger);
// n진수로 생성
BigInteger nBigInteger1 = new BigInteger("FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF", 16); // 16진수
System.out.println("16진수로 선언 : " + nBigInteger1);
BigInteger nBigInteger2 = new BigInteger("00010010010010001111", 2);
System.out.println("2진수로 선언 : " + nBigInteger2);
}
}
/*
출력
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~BIG INTEGER~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
-----------------BigInteger 선언-----------------
문열로 선언 : 111111111111111111111
숫자로 선언 : 222222222
16진수로 선언 : 79228162514264337593543950335
2진수로 선언 : 74895
-----------------BigInteger 형 변환-----------------
int -> BigInteger : 1000000000
BigInteger -> int : 1000000000
BigInteger -> long : 1000000000
BigInteger -> float : 1.0E9
BigInteger -> double : 1.0E9
BigInteger -> String : 1000000000
-----------------BigInteger 연산-----------------
덧셈 BigInteger.add : 222222222222
뺄셈 BigInteger.subtract : 0
곱셈 BigInteger.multiply : 12345679012320987654321
나눗셈 BigInteger.divide : 1
나머지 BigInteger.remainder : 0
-----------------BigInteger 비트 연산-----------------
BitCount : 8
BitLength : 10
testBit : true
setBit : 5114
clearBit : 1010
flipBit : 1019
and : 1
or : 23
xor : 22
not : -8
andNot : 16
shiftLeft : 34
shiftRight : 8
-----------------BigInteger 숫자 비교-----------------
compareTo : -1
-----------------BigInteger 상수-----------------
BigInteger.ZERO : 0
BigInteger.ONE : 1
BigInteger.TWO : 2
BigInteger.TEN : 10
BigInteger.valueOf를 이용한 덧셈 : 30
BigInteger.TEN을 이용한 덧셈 : 30
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~BIG DECIMAL~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
-----------------BigDecimal 선언-----------------
문자열로 선언 : 123.456
double로 선언 : 123.4560000000000030695446184836328029632568359375
valueOf로 선언 : 123.456
소수점 아래자리수 지정 : 123.456
-----------------BigDecimal 형변환-----------------
int -> BigDecimal : 123.456789
BigDecimal -> int : 123
BigDecimal -> long : 123
BigDecimal -> float : 123.45679
BigDecimal -> double : 123.456789
BigDecimal -> String : 123.456789
-----------------BigDecimal 연산-----------------
덧셈 BigDecimal.add :110.12345
뺄셈 BigDecimal.subtract :90.12345
곱셈 BigDecimal.multiply :1001.23450
나눗셈 BigDecimal.divide :10.012345
나머지 BigDecimal.remainder :0.12345
-----------------BigDecimal 숫자 비교-----------------
-1
-----------------BigDecimal 정밀도 값-----------------
정밀도 bigDecimal.precision : 9
지수값(스케일) bigDecimal.scale : 4
부호 bigDecimal.signum : -1
-----------------BigDecimal 지수 제거-----------------
지수 붙은 BigDecimal : 1.0E+7
지수 제거된 BigDecimal : 10000000
-----------------BigDecimal Exception 예시-----------------
ArithmeticException 발생
-----------------BigDecimal Exception 해결 방법-----------------
ArithmeticException Result
3.67
-----------------BigDecimal 반올림 정책-----------------
bigDecimal1.divide(bigDecimal2) -> ArithmeticException
반올림 정책으로 나누어 떨어집니다.
실수 값과 반올림 정책을 이용 : 3
실수 값, 소수점 자리, 반올림 정책 이용 : 3.333333
-----------------BigDecimal setScale 이용-----------------
setScale을 이용하여 소수점 첫 번째까지 표현, 두번째 자리에서 반올림 지정 : 12.4
setScale을 이용하여 소수점 이하 모두 제거하고 올림 지정 : 13
setScale을 이용하여 음수인 경우는 특정 자릿수 이하 제거 지정 : -12.3
setScale을 이용하여 특정 자릿수 이하 버림 지정 : 12.3
12.35
입력 값을 setScale을 이용하여 소수점 첫 번째까지 표현, 두번째 자리에서 반올림 지정 : 12.4
-----------------BigDecimal MathContext 이용-----------------
MathContext을 이용하여 전체 자리수를 7개로 제한하고 HALF_EVEN 반올림을 적용 : 3.333333
MathContext을 이용하여 전체 자리수를 16개로 제한하고 HALF_EVEN 반올림을 적용 : 3.333333333333333
MathContext을 이용하여 전체 자리수를 34개로 제한하고 HALF_EVEN 반올림을 적용한 : 3.333333333333333333333333333333333
MathContext을 // 전체 자리수를 제한하지 않게 적용 -> ArithmeticException 예외 발생 : bigDecimal1.divide(bigDecimal2, MathContext.UNLIMITED)
*/'JAVA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [JAVA] - List의 요소 위치 바꾸기 (swap) (2) | 2024.07.16 |
|---|---|
| [JAVA] - 자바 제네릭 프로그래밍이란? (0) | 2024.06.14 |
| [JAVA] - indexOf, lastIndexOf 특정 문자 위치 찾기 (0) | 2024.05.31 |
| [JAVA] - Stream API 이해 6 (0) | 2024.05.31 |
| [JAVA] - Stream API 이해 5 (0) | 2024.05.30 |
